A robotic-arm-bearing is a highly specialized mechanical component designed to support smooth, precise, and controlled movement inside robotic joints. In modern automation, the quality of the bearing used within a robotic arm directly determines how accurately and efficiently the system performs.
Understanding Why the Robotic Arm Bearing Matters?
Every motion, rotation, and load transfer depends on the bearing’s ability to reduce friction, maintain alignment, and withstand continuous operation. Whether used in industrial assembly, automotive manufacturing, medical robotics, aerospace mechanisms, or high-speed pick-and-place systems, robotic arm bearing play an essential role in ensuring long-term reliability and operational stability.
Unlike standard bearings used in general machinery, robotic-arm bearings are engineered with extremely tight tolerances, higher rigidity, and superior resistance to wear. They are built to handle complex combinations of radial, axial, and moment loads while maintaining predictable and repeatable motion.
As industries increasingly rely on robots for precision tasks, the demand for high-quality bearings becomes more critical. A well-engineered robotic-arm-bearing not only improves motion accuracy but also prevents downtime, reduces vibration, and enhances the overall lifespan of the robotic system. This makes it a fundamental component for any application requiring consistent performance and high precision.

Robotic arm bearing are engineered with high precision to support rotational or linear motion inside robotic joints. Unlike conventional bearings used in general machinery, robotic-arm-bearings are manufactured with tighter tolerances and superior rigidity, allowing robots to maintain consistent accuracy.
Their primary purpose is to reduce friction, support dynamic loads, and allow robotic joints to move smoothly without vibration. When these bearings fail, robots can no longer maintain accurate movement, resulting in production errors and costly downtime. This is why industries that rely on automation prioritize the use of specialized robotic-arm-bearings instead of standard industrial bearings.
Robotic bearings also help ensure reliability and safety. Whether a robot is handling micro-component placement in electronics or lifting heavy materials in manufacturing, stable joint performance prevents hazardous motion errors.
High-precision bearings also provide better efficiency, reducing energy losses caused by friction. This makes them vital not only for performance but also for long-term operational cost savings.
Types of Robotic Arm Bearings and Their Applications
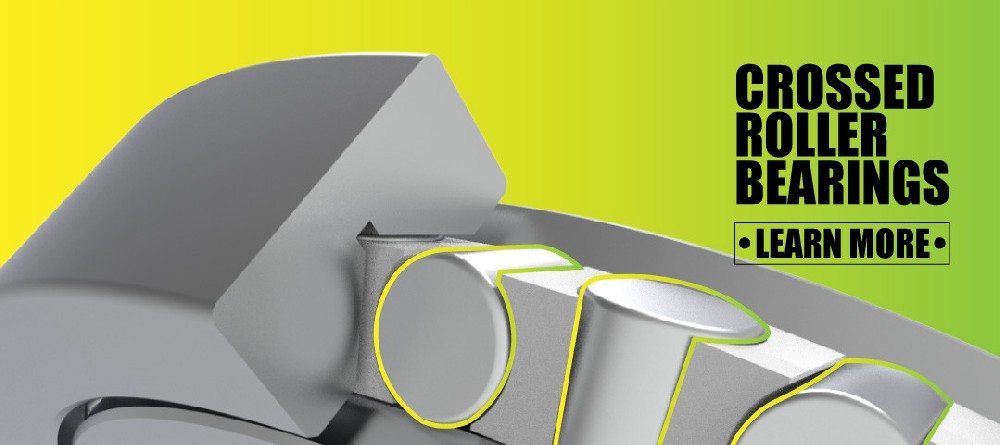
Robotic-arm-bearings are available in several specialized designs, each created to meet the requirements of different robotic systems. The most commonly used types include crossed roller bearings, thin section bearings, angular contact bearings, spherical plain bearings, and hybrid ceramic bearings. Understanding their performance characteristics helps in selecting the best option for your robotic arm.
Crossed roller bearings are widely used in industrial robots because they offer excellent rigidity and extremely high rotational accuracy. They can support radial, axial, and moment loads simultaneously, making them ideal for multi-axis robotic arms.
Thin-section bearings, on the other hand, are compact and lightweight, designed primarily for robots with limited internal space. They maintain smooth motion with minimal torque, making them suitable for medical and small-scale automation robots.
Angular contact bearings provide reliable performance in high-speed applications, while spherical plain bearings handle misalignment in dynamic environments. Hybrid ceramic bearings combine steel rings with ceramic rolling elements, reducing heat and friction, making them suitable for high-speed and cleanroom applications.
Comparison Table of Common Robotic Arm Bearings
| 轴承类型 | Best Application | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 交叉滚子轴承 | Industrial robotic arms, multi-axis robots | High precision, handles combined loads | Higher cost compared to standard bearings |
| Thin Section Bearings | Compact robots, medical robotic arms | Lightweight, smooth rotation | Lower load capacity |
| 角接触轴承 | High-speed robotic joints | Stable at high speeds | Requires controlled lubrication |
| Spherical Plain Bearings | Misalignment-prone robotic systems | Handles irregular load paths | Less precise than crossed rollers |
| 混合陶瓷轴承 | High-speed, cleanroom robots | Low heat, reduced friction | Expensive compared to steel bearings |
Key Performance Characteristics of a High-Quality Robotic Arm Bearing
High-quality robotic-arm bearings are defined by several essential characteristics. The first of these is ultra-low friction, which helps reduce energy consumption and keeps rotational movement smooth. Low friction ensures that robotic joints move with minimal resistance, improving efficiency and reducing wear over time.
Another critical factor is precision tolerance. High-precision bearings are produced with extremely tight dimensional control, enabling stable and vibration-free operation. This makes them suitable for robots requiring sub-millimeter accuracy.
Another defining feature is zero or extremely minimal backlash. Backlash refers to unwanted movement within a joint, which can significantly impact positioning accuracy. High-precision crossed roller and angular contact bearings are often used to achieve near-zero backlash. Load-handling capability is equally important.
Robotic arms experience combined axial, radial, and moment loads, and only bearings engineered for multi-directional forces can maintain stable operation. Bearings made for robotic applications also offer long service life, contamination resistance, and consistent performance under repetitive cycles.
Read also: Robot Arm Bearings: How High Precision Boosts Robot Accuracy
How Robotic-Arm-Bearing Improve Automation Performance?
The performance of a robotic arm is directly connected to the quality of the bearing it uses. High-precision bearings enhance motion control by ensuring smooth, predictable movement. This allows robots to achieve consistent cycle times and maintain productivity across long shifts. Accurate positioning is also supported by robust bearings that reduce micro-errors during rotation. This level of precision is essential for industries such as electronics manufacturing, where even a slight misalignment can cause product defects.
Additionally, robotic arm bearing improve speed and efficiency. Low-friction designs reduce heat buildup, allowing robots to operate at higher speeds without excessive wear. This results in faster cycle completion and improved output. Bearings also reduce maintenance costs by offering longer service life.
When bearings fail prematurely, they disrupt entire production lines; therefore, investing in reliable robotic bearings ensures stable and long-term operation. Better bearing performance also enhances safety by eliminating sudden jerk motions that can damage equipment or products.
Problems Caused by Low-Quality Bearings
Robotic systems experience multiple issues when low-quality bearings are used. Excessive heat buildup due to poor lubrication or high friction is one of the most common problems. Heat accelerates wear and causes premature failure. Backlash is another issue, leading to inaccurate positioning and compromised product quality.
Vibration and noise are also common symptoms of inferior bearings, which can damage other components in the robotic system. Contamination, misalignment, and improper loading further reduce bearing lifespan. These problems not only reduce productivity but also increase operational costs due to repeated maintenance.
Maintenance Practices That Extend Bearing Life
Proper lubrication is the most important factor in extending bearing life. Using high-quality lubricants at controlled intervals prevents friction and wear. Temperature monitoring is also crucial because a spike in heat indicates internal issues.
Keeping bearings clean and free of dust or debris significantly improves lifespan. Bearings must be installed according to manufacturer specifications, and load limits should never be exceeded. Modern robots often use sensors to monitor vibration and temperature, enabling early detection of problems before failure occurs.
Applications of Robotic Arm Bearing Across Industries
Robotic-arm-bearings are widely used in manufacturing robots, automotive welding systems, pick-and-place machines, food packaging lines, logistics automation, and electronic assembly.
In the medical field, high-precision bearings ensure controlled and delicate movement in robotic surgery systems. Aerospace and defense sectors use them in advanced robotic manipulators, while cleanroom robots depend on contamination-resistant bearings.
With robotics expanding into agriculture, construction, and warehousing, the demand for high-quality bearings continues to grow worldwide. For more details visit 这里!

常见问题 (FAQ)
Q1: What is the most commonly used bearing in robotic arms?
一个: Crossed roller bearings are the most widely used due to their exceptional rigidity and ability to handle combined loads.
Q2: How long do robotic arm bearing last?
一个: They can last between twenty thousand and forty thousand hours depending on load, lubrication, and environment.
Q3: Can standard industrial bearings be used in robotic joints?
一个: Standard bearings lack the precision and low-backlash performance required for robotic applications.
Q4: What causes premature bearing failure in robotic arms?
一个: Contamination, poor lubrication, overload, misalignment, and use of low-grade materials are primary causes.
Q5: Are ceramic bearings suitable for robotics?
一个: Yes. Hybrid ceramic bearings offer lower friction, reduced heat, and longer service life, especially in high-speed robotic applications.
结论
一个 robotic arm bearing is far more than a simple mechanical component; it is the foundation of precision, stability, and long-term performance in any robotic system. The efficiency of industrial automation, the reliability of high-speed operations, and the accuracy of delicate robotic tasks all depend on the quality of the bearings supporting each joint.
By selecting bearings engineered for low friction, high rigidity, minimal backlash, and consistent load handling, manufacturers can significantly improve the durability and accuracy of their robotic arms.
Proper installation, correct lubrication, and condition monitoring further extend the lifespan of these critical components. As robotics continues to advance across industries, investing in high-quality robotic-arm bearings becomes essential for achieving smooth motion, predictable performance, and reduced downtime.
For any application demanding precision and reliability, choosing the right bearing is a strategic decision that directly impacts operational success.