Robot arm bearings are critical components that allow robotic arms to move smoothly, accurately, and safely. Whether in industrial automation, manufacturing, or research, these bearings enable precise motion for complex tasks. Understanding the different types of 机器人手臂轴承 and their functions is essential for engineers, designers, and automation professionals.
Introduction to Robot Arm Bearings
A robotic arm is made of multiple joints, linear axes, and rotational mechanisms. Each of these components relies on bearings to reduce friction, support loads, and maintain stability. Bearings allow robots to perform linear, rotational, and arc movements with precision.
From gantry robots to collaborative robotic arms, proper bearing selection ensures smooth motion, long-term reliability, and consistent accuracy.
Key Types of Bearings Used in Robot Arms
Robot arms use various bearings depending on the joint type, motion, and load requirements. Here are the main types:

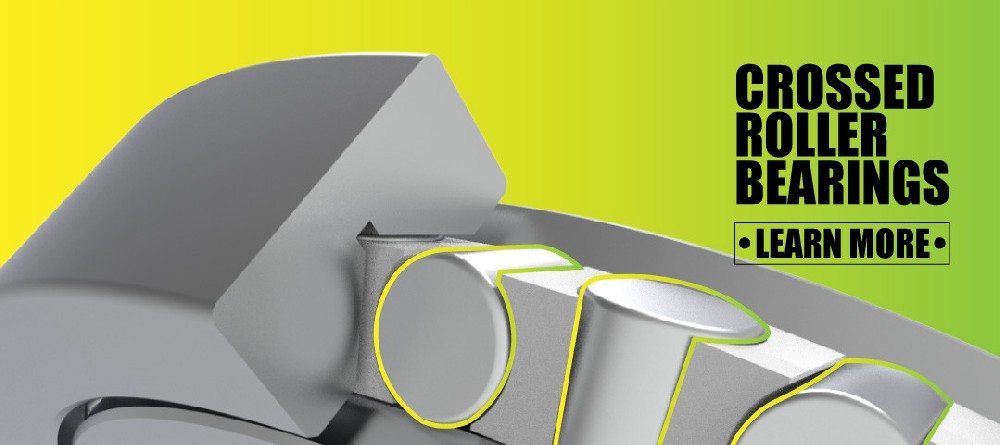
交叉滚子轴承
Function: Crossed roller bearings support loads in multiple directions simultaneously and provide high rotational accuracy.
Application: Commonly used in robot wrists and rotational joints, especially in precision industrial arms.
Thin Section Bearings
Function: Thin section bearings offer low weight and a small cross-section while providing significant load support.
Application: Ideal for robotic joints like elbows and wrists where space is limited.
RV Reducer (Precision Joint) Bearings
Function: RV reducer bearings are designed for high rigidity and precision in rotary joints.
Application: Often integrated into robot arm joints where exact positioning is required.
Harmonic Reducer Bearings
Function: These flexible bearings transmit motion through a controlled deformation mechanism.
Application: Suitable for torque-sensitive robot joints requiring smooth motion.
Spherical Plain Bearings
Function: Spherical plain bearings accommodate misalignment and pivoting motion.
Application: Used in robot joints that experience oscillating or pivoting angles.
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Function: These bearings automatically adjust to shaft misalignment.
Application: Applied in joints that experience dynamic load shifts and minor misalignments.
Linear Bearings and Guides
Function: Linear bearings enable smooth straight-line motion along an axis.
Application: Essential in gantry robots, Cartesian robots, and other systems requiring precise linear travel.
How Robot Arm Bearings Support Motion
Robot arm bearings play a pivotal role in enabling three types of motion:
-
Linear Motion: Bearings allow robotic arms to move along straight paths with minimal friction.
-
Rotational Motion: Bearings provide smooth rotation in joints and wrists.
-
Arc or Pivot Motion: Specialized bearings support oscillation and pivoting angles, essential for multi-axis robots.
The correct combination of precision bearings, joint bearings, and linear bearings ensures robots can operate at high speed, with minimal wear and maximum reliability.
Functional Roles of Robot Arm Bearings
-
Reduce Friction: Bearings allow smooth movement with less energy consumption.
-
Support Loads: They carry axial, radial, and combined loads during robotic operations.
-
Maintain Accuracy: High-precision bearings ensure repeatable motion and positioning.
-
Extend Lifespan: Quality bearings reduce wear and tear on robot joints and components.
-
Enhance Safety: Proper bearings prevent unexpected failures that could disrupt industrial processes.
Choosing the Right Bearing for Robot Arms
Selecting the correct robot arm bearing involves considering:
-
Load Requirements: Weight and torque the bearing must handle.
-
Motion Type: Linear, rotational, or pivoting movements.
-
Space Constraints: Available room for bearing installation.
-
环境条件: Temperature, humidity, dust, and lubrication needs.
-
Accuracy and Precision: High-precision bearings for sensitive applications.
Maintenance Tips for Robot Arm Bearings
-
Regular inspection for wear or misalignment.
-
Proper lubrication using recommended oils or greases.
-
Replace worn bearings before they affect precision.
-
Avoid contamination with dust or debris to extend lifespan.
Routine maintenance keeps robotic arms operating smoothly and safely, reducing downtime and repair costs.
结论
Robot arm bearings are essential for smooth, accurate, and reliable motion in industrial robots. By understanding types of bearings like crossed roller, thin section, RV reducer, spherical plain, and linear bearings, engineers can design robotic arms that are efficient, durable, and precise.
恰当的 bearing selection, installation, and maintenance ensure the longevity and performance of robot arms, supporting automation in industries ranging from manufacturing to medical robotics.