Angular contact ball bearing vs deep groove ball bearing are two of the most commonly used rolling bearings in industrial, automotive, and precision machinery. While both reduce friction and support rotating shafts, their design, load handling, and applications differ significantly. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right bearing for performance, reliability, and service life.
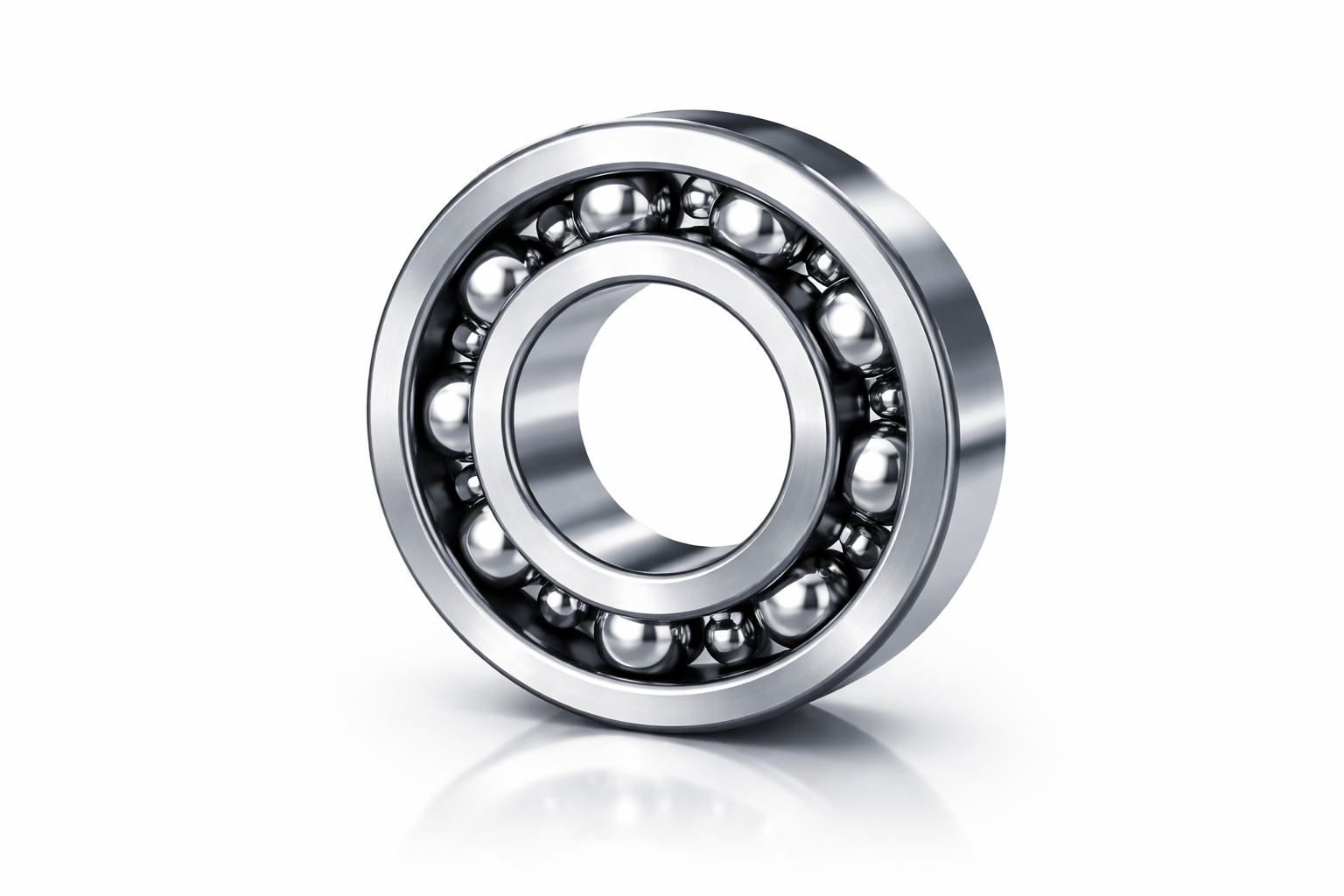

What Is a Deep Groove Ball Bearing?
Design and Structure
A deep groove ball bearing has deep raceway grooves and symmetrical inner and outer rings. This design allows smooth rolling motion with minimal friction. It is typically a single-row bearing but also available in double-row variants.
Load Handling Capability
Deep groove ball bearings are mainly designed for radial loads, but they can also support limited axial loads in both directions. However, axial load capacity is not their primary strength.
Common Applications
-
Electric motors
-
Fans and blowers
-
Pumps
-
Household appliances
-
Automotive components
Key Advantages
-
Simple design and easy installation
-
Low friction and quiet operation
-
Suitable for high speeds
-
Cost-effective and widely available
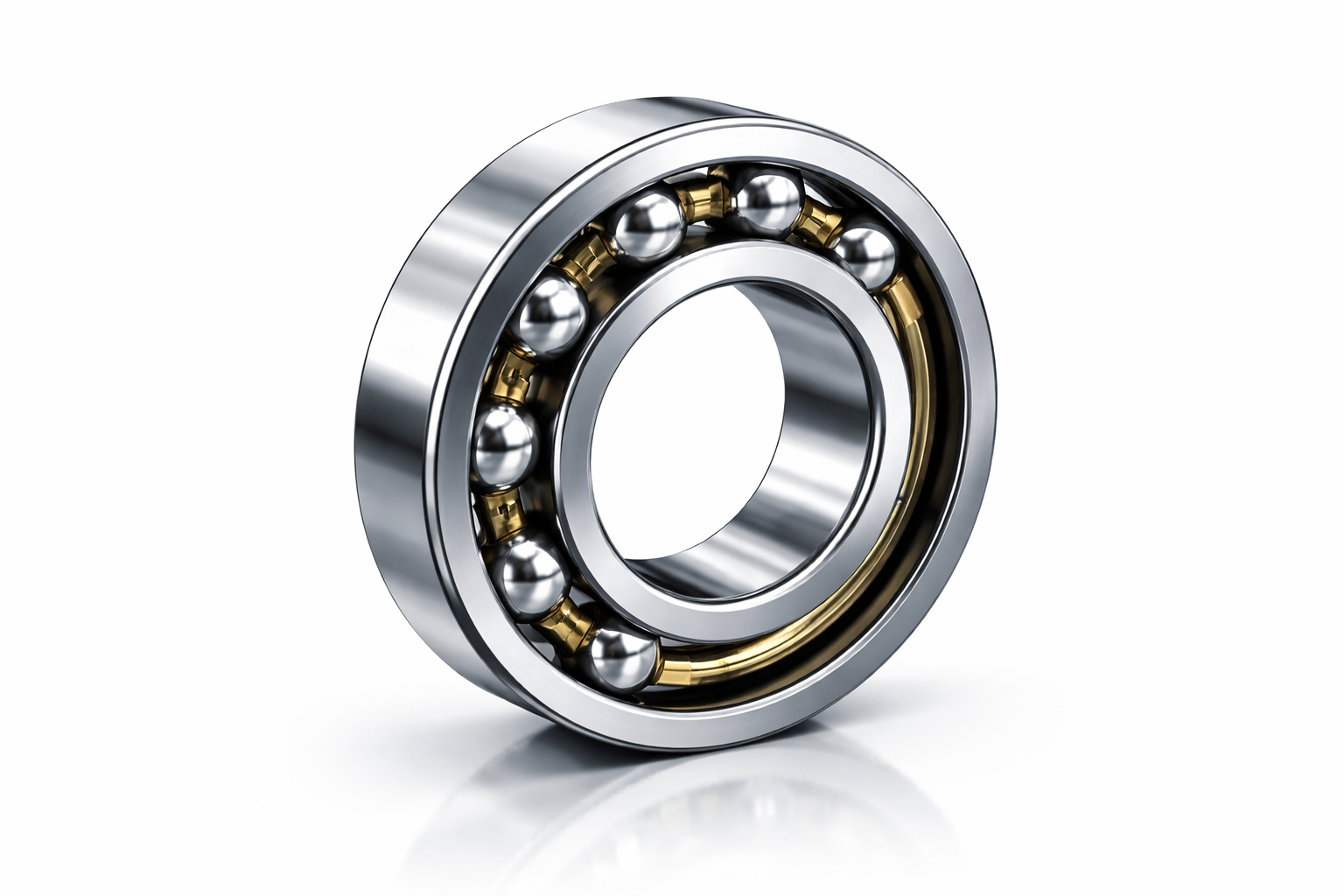

What Is an Angular Contact Ball Bearing?
Design and Contact Angle
An angular contact ball bearing features raceways that are offset relative to each other, creating a contact angle. This angle allows the bearing to carry axial loads in addition to radial loads.
Axial and Combined Load Capacity
Angular contact bearings are specifically designed to handle combined radial and axial loads. The axial load capacity increases with a larger contact angle. These bearings are often mounted in pairs or sets to handle axial loads in both directions.
Common Applications
-
CNC machine spindles
-
Gearboxes
-
Compressors
-
Pumps with axial thrust
-
High-precision machinery
Key Advantages
-
High axial load capacity
-
Better stiffness and precision
-
Suitable for high-speed and high-load applications
-
Excellent performance under combined loads
Key Differences Between Angular Contact Ball Bearing vs Deep Groove Ball Bearing
Radial Load vs Axial Load Handling
Deep groove ball bearings primarily handle radial loads, with limited axial capacity. Angular contact ball bearings are designed for axial loads and combined loads, making them suitable for thrust-heavy applications.
Contact Angle and Load Direction
Deep groove bearings have zero contact angle, so load transmission is mostly radial. Angular contact bearings have a defined contact angle (15°, 25°, 30°, or more), allowing efficient axial load transfer.
Speed and Performance
Both bearing types support high rotational speeds. However, angular contact bearings perform better in high-speed precision applications where axial loads are present.
Installation and Mounting Requirements
Deep groove ball bearings are easy to install and do not require special arrangements. Angular contact bearings often need paired mounting (back-to-back or face-to-face) and precise preload control.
Application Suitability
-
Deep groove ball bearing: general-purpose, low to moderate load applications
-
Angular contact ball bearing: high-load, high-precision, axial force applications
Which Bearing Should You Choose?
Based on Load Requirements
Choose a deep groove ball bearing for pure radial or light axial loads. Choose an angular contact ball bearing for significant axial or combined loads.
Based on Speed and Precision
For standard high-speed operation, deep groove bearings are sufficient. For high precision, stiffness, and spindle performance, angular contact bearings are preferred.
Based on Application Type
-
Motors, fans, appliances → Deep groove ball bearing
-
Machine tools, pumps with thrust, gear systems → Angular contact ball bearing
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Deep groove bearings are generally lower cost and easier to maintain. Angular contact bearings may cost more due to precision design but offer longer service life in demanding applications.
Maintenance and Service Life Comparison
Both bearing types require proper lubrication and alignment. Deep groove bearings are more tolerant of minor misalignment. Angular contact bearings require accurate mounting, preload control, and clean lubrication to achieve maximum bearing life.
Conclusion
The choice between an angular contact ball bearing and a deep groove ball bearing depends on load direction, axial force, speed, and application precision. Deep groove ball bearings are ideal for general-purpose use, while angular contact ball bearings are the correct solution for high axial loads and precision-critical systems. Selecting the right bearing ensures better performance, reduced downtime, and longer operational life.